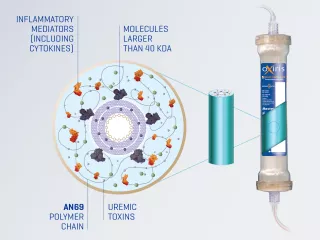
Oxiris Filterset
Oxiris is the ONLY blood purification filterset to effectively remove inflammatory mediators, endotoxin, fluid and uremic toxins simultaneously.1-5
Sepsis is a major and growing global healthcare challenge.6-8 Blood purification therapies may help improve outcomes.1,3,9-11
~30% of ICU patients have sepsis12
~50% of patients with sepsis have kidney dysfunction or failure13,14
~45% of patients with sepsis die within 1 year7,8,15
Compatible Products
Acute Therapy Systems
CRRT Solutions
Filtersets & Catheters
Digital Solutions
The ICU is a complex environment that could benefit from ways to simplify therapy delivery
Versatile innovation
The Oxiris filterset can be used to deliver haemoperfusion to reduce elevated levels of inflammatory mediators/endotoxins and/or to deliver any CRRT modality (SCUF, CVVH, CVVHD, CVVHDF) to provide uremic toxin removal and support fluid management.5 Note: CVVH, Continuous Veno-Venous Haemofiltration; CVVHD, Continuous Veno-Venous HaemoDialysis; CVVHDF, Continuous Veno-Venous Haemodiafiltration; SCUF, Slow Continuous UltraFiltration
Inflammatory mediator removal
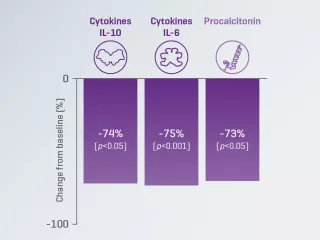
A prospective, multicenter, observational study reported a significant decrease from baseline in serum IL-6 levels in patients with COVID-19 treated with the Oxiris filterset.2
Endotoxin removal
A randomised, crossover study reported significantly greater changes from baseline in endotoxin level with the Oxiris filterset, compared to the AN69ST filterset in patients with septic-shock-associated AKI.3
Versatile simplification
The Oxiris filterset is designed to simplify blood purification therapy delivery for patients requiring both cytokine/endotoxin removal and CRRT, which may free up nursing time. The Oxiris filterset is part of a pre-connected set for simplicity. The closed system includes a filter membrane pre-connected to the colour-coded tubing, minimising setup steps and reducing potential for touch contamination.5,16
87%
4.5
8.3%
The COVID-19 pandemic
- Systemic inflammation in patients with COVID-19 can lead to multi-organ failure, including AKI.22,23
- Blood purification techniques have been shown to remove cytokines, endotoxin and circulating viral particles in patients with COVID-19.24
- Blood purification is the only therapy that may effectively remove inflammatory mediators, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and/or pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs, e.g., endotoxin),2 which may help mitigate progression to multi-organ failure.1,2,9,11,20,21,25
Potential targets for COVID-19 therapies include the removal of cytokines26
Stages of the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle offer potential treatment targets. Potential targets for COVID-19 therapies include anti-inflammatory therapies,27 prevention of membrane fusion and viral cell entry,28 removal of cytokines or prevention of cytokine receptor activation26,28,29 and prevention of RNA translation.28,30-33
Vantive, AN69, Oxiris, Prismaflex and PrisMax are trademarks of Vantive Health LLC or its affiliates.
References
-
Turani F, Barchetta R, Falco M, Busatti S, Weltert L. Continuous renal replacement therapy with the adsorbing filter Oxiris in septic patients: a case series. Blood Purif. 2019;47(3):54-58.
-
Villa G, Romagnoli S, De Rosa S, et al. Blood purification therapy with a hemodiafilter featuring enhanced adsorptive properties for cytokine removal in patients presenting COVID-19: a pilot study. Crit Care. 2020;24:605.
-
Broman ME, Hansson F, Vincent JL, Bodelsson M. Endotoxin and cytokine reducing properties of the oXiris membrane in patients with septic shock: a randomized crossover double-blind study. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0220444.
-
Malard B, Lambert C, Kellum JA. In vitro comparison of the adsorption of inflammatory mediators by blood purification devices. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2018;6:12.
-
Vantive. Oxiris Instructions for Use. 2022.
-
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395:200-211.
-
Karlsson S, Varpula M, Ruokonen E, et al. Incidence, treatment, and outcome of severe sepsis in ICU-treated adults in Finland: the Finnsepsis study. Intensive care medicine. 33. 435-43. 10.1007/s00134-006-0504-z. et al. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33:435-443.
-
van Vught LA, Klein Klouwenberg PM, Spitoni C, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and attributable mortality of secondary infections in the intensive care unit after admission for sepsis. JAMA. 2016;315:1469-1479.
-
Lumlertgul N, Srisawat N. The haemodynamic effects of oXiris haemofilter in septic shock patients requiring renal support: A single-centre experience. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;44:17-24.
-
Cruz DN, Antonelli M, Fumagalli R, et al. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: the EUPHAS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301:2445-2452.
-
Hawchar F, László I, Öveges N, Trásy D, Ondrik Z, Molnar Z. Extracorporeal cytokine adsorption in septic shock: a proof of concept randomized, controlled pilot study. J Crit Care. 2019;49:172-178.
-
Sakr Y, Jaschinski U, Wittebole X, et al. Sepsis in intensive care unit patients: worldwide data from the Intensive Care over Nations Audit. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2018;5:ofy313.
-
Yébenes JC, Ruiz-Rodriguez JC, Ferrer R, et al. Epidemiology of sepsis in Catalonia: analysis of incidence and outcomes in a European setting. Ann Intensive Care. 2017;7:19.
-
Mayr FB, Yende S, Linde-Zwirble WT, et al. Infection rate and acute organ dysfunction risk as explanations for racial differences in severe sepsis. JAMA. 2010;303:2495-2503.
-
Prescott HC, Osterholzer JJ, Langa KM, Angus DC, Iwashyna TJ. Late mortality after sepsis: propensity matched cohort study. BMJ. 2016;353:i2375.
-
Vantive. Oxiris Specification Sheet. 2022.
-
Monard C, Rimmelé T, Ronco C. Extracorporeal blood purification therapies for sepsis. Blood Purif. 2019;47(Suppl. 3):2-15.
-
Thomas M, Moriyama K, Ledebo I. AN69: Evolution of the world's first high permeability membrane. Contrib Nephrol. 2011;173:119-129.
-
Hattori N, Oda S. Cytokine-adsorbing hemofilter: old but new modality for septic acute kidney injury. Ren Repl Ther. 2016;2:41.
-
Schwindenhammer V, Girardot T, Chaulier K, et al. oXiris® use in septic shock: experience of two French centres. Blood Purif. 2019;47(suppl 3):29-35.
-
Nassiri AA, Hakemi MS, Miri MM, Shahrami R, Koomleh AA, Sabaghian T. Blood purification with CytoSorb in critically ill COVID-19 patients: a case series of 26 patients. Artif Organs. 2021;45:1338-1347.
-
Lavillegrand JR, Garnier M, Spaeth A, et al. Elevated plasma IL-6 and CRP levels are associated with adverse clinical outcomes and death in critically ill SARS-CoV-2 patients: inflammatory response of SARS-CoV-2 patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2021;11:9.
-
Anderberg S, Luther T, Berglund M, et al. Increased levels of plasma cytokines and correlations to organ failure and 30-day mortality in critically ill Covid-19 patients. Cytokine. 2021;138:155389.
-
Nadim MK, Forni LG, Mehta RL, et al. COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: consensus report of the 25th Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) Workgroup. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16:747-764.
-
Rosalia RA, Ugurov P, Neziri D, et al. Extracorporeal blood purification in moderate and severe COVID-19 patients: a prospective cohort study. Blood Purif. 2021;51:233-242.
-
Ronco C, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, et al. Extracorporeal blood purification and organ support in the critically ill patient during COVID-19 pandemic: expert review and recommendation. Blood Purif. 2021;50(1):17-27.
-
RECOVERY Collaborative Group, Horby P, Lim WS, et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):693-704.
-
Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1824-1836.
-
Huet T, Beaussier H, Voisin O, et al. Anakinra for severe forms of COVID-19: a cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2:e393-400.
-
Hung IF, Lung KC, Tso EY, et al. Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir-ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1695-704.
-
Sang P, Tia S, Meng Z, Yang L. Anti-HIV drug repurposing against SARS-CoV-2. RSC Adv. 2020;10:15775-15783.
-
Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 - final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(19):1813-1826.
-
U.S. National Library of Medicine. NCT04351295. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04351295 (accessed November 2021).